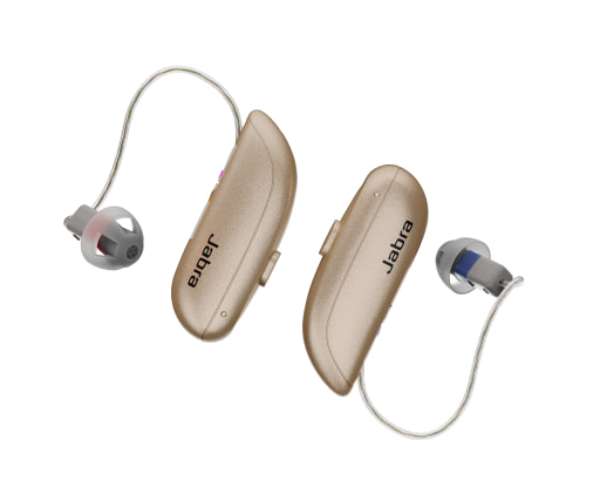
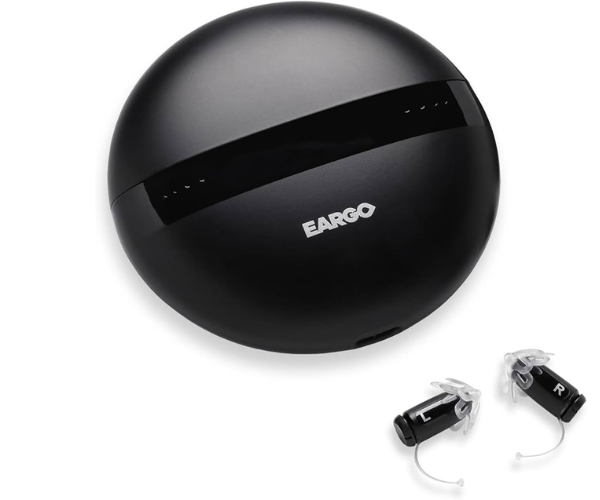
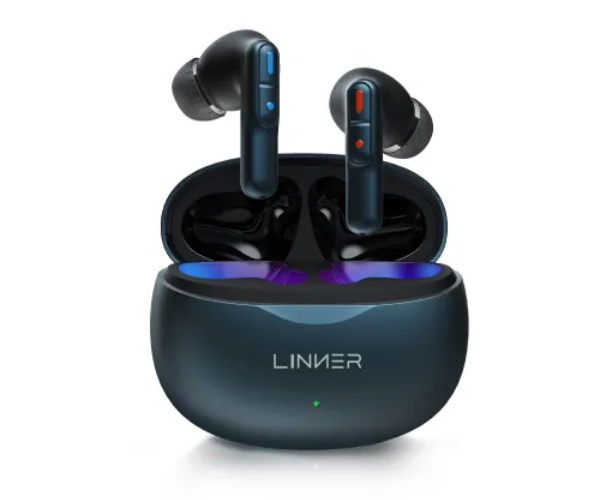
What level of hearing loss requires a hearing aid?
There are five levels of hearing loss, ranging from mild to profound, according to the Hearing Health Foundation (HHF). If you have mild to moderate hearing loss, you may be eligible for personal sound amplification products (PSAPs) or hearing aids, depending on an individual evaluation conducted by a hearing health professional.
How do you clean hearing aids?
It depends on the type of hearing aid you wear, but generally, you can wipe the devices with a damp cloth to remove any larger debris. Then, use a small, gentle brush tool to clean ear wax out of any small holes on the device where it could build up over time.
How long do hearing aids last?
Most high-quality hearing aids typically last three to seven years. Some people will use their hearing aids longer. Manufacturers often stop producing legacy parts required for repairs after five to seven years.
Where do you buy hearing aids?
You can buy hearing aids directly from your audiologist, through a hearing aid dispenser, from stores owned by hearing aid manufacturers and wholesale clubs like Costco.
Does Medicare cover hearing aids?
Medicare and most private insurance plans don’t cover hearing aids. Some plans, including Medicare Advantage, pay for some costs.
The Veterans Administration covers hearing aids in many cases. And many federal workers, including retirees, may have hearing aid benefits through the Federal Employees Health Benefits program.
Where can I find cheap hearing aids?
Speak with an audiologist to learn about the most appropriate hearing aid options for you, and then make your selection based on affordability. Aiming for a less expensive option over one that can address your hearing loss appropriately can lead to the selection of a hearing aid that doesn’t work as well as it should for you.
Do you get a trial period for hearing aids?
Most states require a 30- to 60-day trial period for hearing aids, according to the Federal Trade Commission. During this time, you can return your hearing aids and get most, sometimes all, of your money back. Typically, providers will offer a trial period even in states that don’t require it.
What are the side effects of a hearing aid?
Wearing hearing aids can result in some side effects when not sized or used correctly, including:
- Soreness around the ear where the hearing aid sits
- Skin irritation
- Itchiness in the ear canal
- Trouble hearing properly
- Headaches
- Tinnitus
- Excessive feedback from the hearing aid